While we on Earth suffer from coronavirus, our star — the Sun — is having a lockdown all of its own. The sun has been reported to have a ‘very deep’ solar minimum with 100 days of 2020 not seeing any sunspots on its surface. The sun is heading toward solar minimum now.
Sunspot counts were relatively high in 2014, and now they are sliding toward a low point expected in 2019-2020. Astronomer Dr Tony Phillips said: “Solar Minimum is under way, and it’s a deep one.
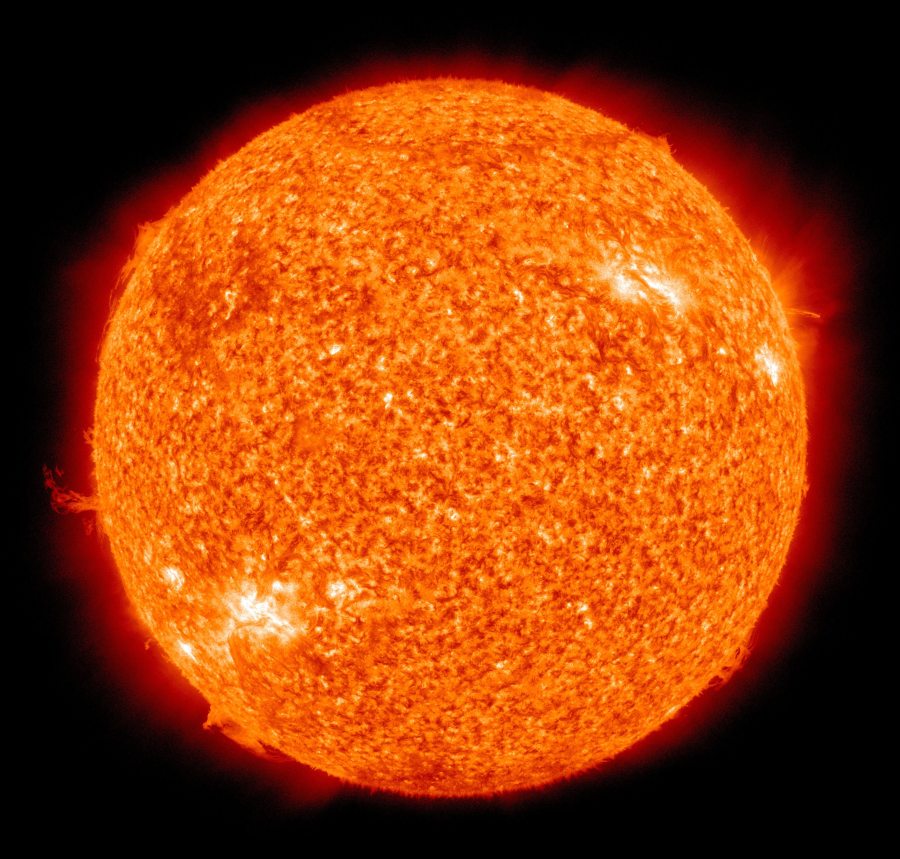
High up in the clear blue noontime sky, the sun appears to be much the same day-in, day-out, year after year. But astronomers have long known that this is not true. The sun does change. Properly-filtered telescopes reveal a fiery disk often speckled with dark sunspots. Sunspots are strongly magnetised, and they crackle with solar flares —magnetic explosions that illuminate Earth with flashes of X-rays and extreme ultraviolet radiation. The sun is a seething mass of activity.
Astronomer Dr Tony Phillips says the current lack of sunspot counts suggests the current solar minimum is one of the ‘deepest’ of the past century. While intense activity such as sunspots and solar flares subside during solar minimum, that doesn’t mean the sun becomes dull. Solar activity simply changes form.

A sunspot is an area of magnetic activity on the surface of the sun — also known as storms — and appear in areas of darkness. They play a huge part in the sun’s activity, including birthing solar flares and coronal mass ejections. Although sunspots seem like tiny specks, they can be colossal in size. Sunspots have been continuously counted each day since 1838, which has allowed solar scientists to describe a repeating pattern in the wax and wane of activity on the Sun’s surface — the solar cycle.
The Sun has a cycle that lasts between nine and 14 years — typically around 11 years, on average — and right now we’re in the trough. At the peak of that cycle — called solar maximum — the Sun produces more electrons and protons as huge solar flares and coronal mass ejections. Just as solar maximum sees many sunspots, the trough of solar minimum features zero sunspots — and that’s what’s going on now. However, it’s been continuing rather longer than expected, which means the Sun is in the midst of a particularly deep solar minimum. Some scientists speculate that this may be the beginning of a periodic solar event called a “grand minimum,” while others say there is insufficient evidence to support that position.
NASA says: solar minimum brings about many changes to our sun, but less solar activity doesn’t make the sun and our space environment any less interesting.
NASA first recorded no activity on the sun last summer and it is thought to have continued to be without sunspots ever since. Solar minimums usually consist of 12 months of little sunspot activity.
The most infamous happened between 1645 to 1715 when a “Maunder Minimum” saw a prolonged sunspot minimum when sunspots were very rare for an extended period. Nasa scientists fear it could be a repeat of the “Dalton Minimum”, which happened between 1790 and 1830 — leading to periods of brutal cold, crop loss, famine and powerful volcanic eruptions. Temperatures plummeted by up to 2ºC over 20 years, devastating the world’s food production. Some people have linked the Maunder Minimum’s temporary cooling effect to decreased solar activity, but that change was more likely influenced by increased volcanic activity and ocean circulation shifts, according to NASA.
During a grand minimum, solar magnetism diminishes, sunspots appear infrequently and less ultraviolet radiation reaches Earth. Grand minimums can last several decades to centuries. The largest recent event happened during the “Little Ice Age” (13th to mid-19th century): the “Maunder Minimum,” an extended period of time between 1645 and 1715, when there were few sunspots.

The idea of solar minimums affecting life on Earth is an on-going debate with some scientists believing it can affect the weather and earthquakes, while others argue it has little impact on our planet. Some scientists have linked previous solar minimums to dramatic drops in Earth’s temperature, including causing what was known as the ‘little ice age’ in the 1600s — some even fear it may happen again.
While these things are still ongoing debates, one thing that NASA did find to happen during solar minimum was an increased number of galactic cosmic rays that reach Earth’s upper atmosphere. Galactic cosmic rays are high energy particles accelerated toward the solar system by distant supernova explosions and other violent events in the galaxy.
During solar minimum, the effects of Earth’s upper atmosphere on satellites in low Earth orbit changes too. This happens due to the sun’s magnetic field weakening during solar minimum. Meanwhile, humans on earth are still protected by the earth’s magnetic fields that shield us from the rays.
So far this year the sun has been “blank” with no sunspots 76 percent of the time, a rate surpassed only once before in the Space Age — last year, when it was 77 percent blank. However, even a prolonged “Grand Solar Minimum” or “Maunder Minimum” would only briefly and minimally offset human-caused warming.
While the uncertainties associated with the anthropogenic greenhouse gas forcing have been studied intensely, the contribution of natural climate drivers (particularly solar variability) to recent and future climate change are still a subject of intense debate.
According to a NASA Global Climate Change blog post, a new Grand Solar Minimum would only serve to offset a few years of warming caused by human activities. The warming caused by the greenhouse gas emissions from the human burning of fossil fuels is six times greater than the possible decades-long cooling from a prolonged Grand Solar Minimum.
Pink elephant in the room: There is no impending “ice age” or “mini ice age” to be caused by an expected reduction in the Sun’s energy output in the next several decades.

Such an enlightening article. Thank you!
LikeLiked by 2 people
Thanks, Leah.
LikeLiked by 2 people
Wow! So, the sun is also in lockdown with us. Is that the reason that we are having hailstorms, earthquakes so frequently! Who knows? Let’s hope we get back to our normal life again soon.
LikeLiked by 2 people
Let’s hope so. Tathastu!
LikeLiked by 1 person
Interesting and knowledge enhancing. If this inaction continues, will we see a reversal of global warming or will it aggravate further??
LikeLiked by 2 people
According to the United Nations’ Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), the current scientific consensus is that long and short-term variations in solar activity play only a very small role in Earth’s climate. Warming from increased levels of human-produced greenhouse gases is actually many times stronger than any effects due to recent variations in solar activity. There’s a pink elephant in the room! 😉
LikeLiked by 1 person
And guess what I studied in geography that a later(I guess the deepest) is also called corona. I have studied about sunspots in geography… Isn’t it true that they appear after a period of some 11 years? And these are originators of solar flares… Also these are relatively cooler regions in sun. Bahut sara knowledge…. Mai toh pura padhte padhte thak gayi.😍😍
LikeLiked by 2 people
Hahaha!
The Sun’s corona is the outermost part of the Sun’s atmosphere. It is usually hidden by the bright light of the Sun’s surface and can be seen during a total solar eclipse. Yes, the solar minimum and maximum are the two extremes of solar cycles with average period of 11 years.
Thanks for your interest and read.
LikeLiked by 2 people
This is something new I have learned today. Thanks for sharing. I had zero clues on this aspect of the sun.
LikeLiked by 2 people
Thanks for your read and retweet.
LikeLiked by 2 people
You are welcome.
LikeLiked by 2 people
Wow. Great post. Sun is also in lockdown. It’s a news.
LikeLiked by 2 people
Thanks for your read and like.
LikeLiked by 1 person
👍
LikeLiked by 2 people
Quite informative! Sunspots occur due to change in the magnetic flux and hence appear in pairs which is therefore suggestive of the the extra energy released from the nuclear fusion of the Hydrogen molecule to become Helium and hence giving out energy in the form of heat, electromagnetic waves etc, etc. The sunspots are formed as a result of the balance in between the energy. So reduced sun spots would mean reduce fusion reaction and hence means reduced hydrogen storage and hence may be sun is just trying to replenish its sources so as to survive the battle against its own extinction.
What I mean to say is that its just like sleeping with reduce activity so as to recover the lost energy as we do, that makes me think that may be Darwin’s “struggle for existence and survival of the fittest theory” does not only apply to what we think or it may actually be more universal.
Hmmm……. This post made my grey cells race.
LikeLiked by 2 people
Thanks, beta. Good thought.
LikeLiked by 1 person
Ohhh another optimism adding to healing earth! Wasn’t knowing this before! Thanks for info
LikeLiked by 2 people
Thanks, Shreya.
LikeLiked by 1 person
It’s good, and fun, to know that the Sun has its own large-scale social restrictions. 🙂
LikeLiked by 1 person
Thanks so much for this wonderful information put into words we all can understand.
LikeLiked by 1 person
Thanks, Geri.
LikeLiked by 1 person